A typical pathway for sound signal transduction
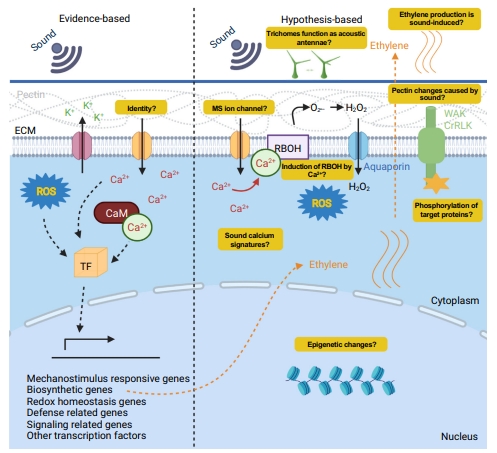
A typical pathway for sound signal transduction
On the left are molecular players and interactions supported by evidence, and on the right are conjectures. Significant gaps in understanding are indicated in yellow. It is demonstrated that sound triggers a cytosolic Ca 2+ surge by activating an unidentified mechanosensitive (MS) Ca 2+ channel. Moreover, K + is transferred to the extracellular matrix (ECM) from the cytosol. A burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) follows. Numerous transcription factors (TFs) that support the differential expression of the gene categories listed in the scheme can be activated by both ROS and Ca2+. It has been proposed that trichomes detect sound and cause nearby cells’ MS ion channels to open. Although MS ion channels may be directly induced by sound, but it is proposed that trichomonas accelerates the process.
